spring 事务
使用
1 | <!--事物管理类--> |
2 | <bean id="dataSourceTransactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> |
3 | <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> |
4 | </bean> |
5 | <!--开启注解模式--> |
6 | <!-- 基于注解的事务管理:事务开启的入口 --> |
7 | <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="dataSourceTransactionManager"/> |
8 | <!--<tx:jta-transaction-manager/>--> |
事物自定义标签
<tx:annotation-driven/> 事物配置的开关,全局搜索,发现在 类 TxNamespaceHandler#init 方法中找打了初始化的方法。
1 | //TxNamespaceHandler |
2 | |
3 | public void init() { |
4 | registerBeanDefinitionParser("advice", new TxAdviceBeanDefinitionParser()); |
5 | registerBeanDefinitionParser("annotation-driven", new AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser()); |
6 | registerBeanDefinitionParser("jta-transaction-manager", new JtaTransactionManagerBeanDefinitionParser()); |
7 | } |
由以上代码可知,spring 会使用 AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser 去解析 annotation-driver
1 | //AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser |
2 | public BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) { |
3 | registerTransactionalEventListenerFactory(parserContext); |
4 | String mode = element.getAttribute("mode"); |
5 | if ("aspectj".equals(mode)) { |
6 | // mode="aspectj" |
7 | registerTransactionAspect(element, parserContext); |
8 | } |
9 | else { |
10 | // mode="proxy" |
11 | AopAutoProxyConfigurer.configureAutoProxyCreator(element, parserContext); |
12 | } |
13 | return null; |
14 | } |
解析中存在对于mode 属性的判断,所以,在spring 事物切入上,我们可以使用如下事物切入方式的配置
1 | <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="dataSourceTransactionManager" modle="aspectj"/>〉 |
注册InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
1 | public static void configureAutoProxyCreator(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) { |
2 | AopNamespaceUtils.registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(parserContext, element); |
3 | |
4 | String txAdvisorBeanName = TransactionManagementConfigUtils.TRANSACTION_ADVISOR_BEAN_NAME; |
5 | if (!parserContext.getRegistry().containsBeanDefinition(txAdvisorBeanName)) { |
6 | Object eleSource = parserContext.extractSource(element); |
7 | |
8 | // Create the TransactionAttributeSource definition. |
9 | RootBeanDefinition sourceDef = new RootBeanDefinition( |
10 | "org.springframework.transaction.annotation.AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource"); |
11 | sourceDef.setSource(eleSource); |
12 | sourceDef.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE); |
13 | String sourceName = parserContext.getReaderContext().registerWithGeneratedName(sourceDef); |
14 | |
15 | // Create the TransactionInterceptor definition. |
16 | RootBeanDefinition interceptorDef = new RootBeanDefinition(TransactionInterceptor.class); |
17 | interceptorDef.setSource(eleSource); |
18 | interceptorDef.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE); |
19 | registerTransactionManager(element, interceptorDef); |
20 | interceptorDef.getPropertyValues().add("transactionAttributeSource", new RuntimeBeanReference(sourceName)); |
21 | String interceptorName = parserContext.getReaderContext().registerWithGeneratedName(interceptorDef); |
22 | |
23 | // Create the TransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor definition. |
24 | RootBeanDefinition advisorDef = new RootBeanDefinition(BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor.class); |
25 | advisorDef.setSource(eleSource); |
26 | advisorDef.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE); |
27 | advisorDef.getPropertyValues().add("transactionAttributeSource", new RuntimeBeanReference(sourceName)); |
28 | advisorDef.getPropertyValues().add("adviceBeanName", interceptorName); |
29 | if (element.hasAttribute("order")) { |
30 | advisorDef.getPropertyValues().add("order", element.getAttribute("order")); |
31 | } |
32 | parserContext.getRegistry().registerBeanDefinition(txAdvisorBeanName, advisorDef); |
33 | |
34 | CompositeComponentDefinition compositeDef = new CompositeComponentDefinition(element.getTagName(), eleSource); |
35 | compositeDef.addNestedComponent(new BeanComponentDefinition(sourceDef, sourceName)); |
36 | compositeDef.addNestedComponent(new BeanComponentDefinition(interceptorDef, interceptorName)); |
37 | compositeDef.addNestedComponent(new BeanComponentDefinition(advisorDef, txAdvisorBeanName)); |
38 | parserContext.registerComponent(compositeDef); |
39 | } |
- 上述代码中我们看到注册了代理类 及三个bean
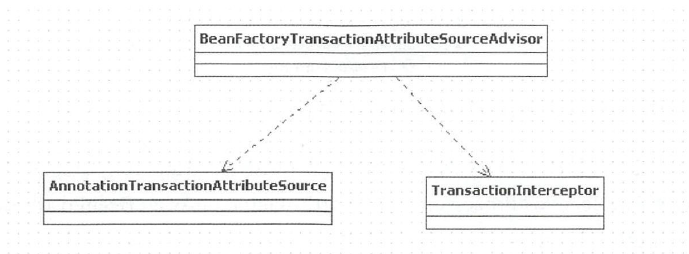
AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser,TransactionInterceptor,BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor,这三个bean 支撑了 spring 的整个事物。
AopNamespaceUtils.registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(parserContext, element); 分析
- InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator 类结构
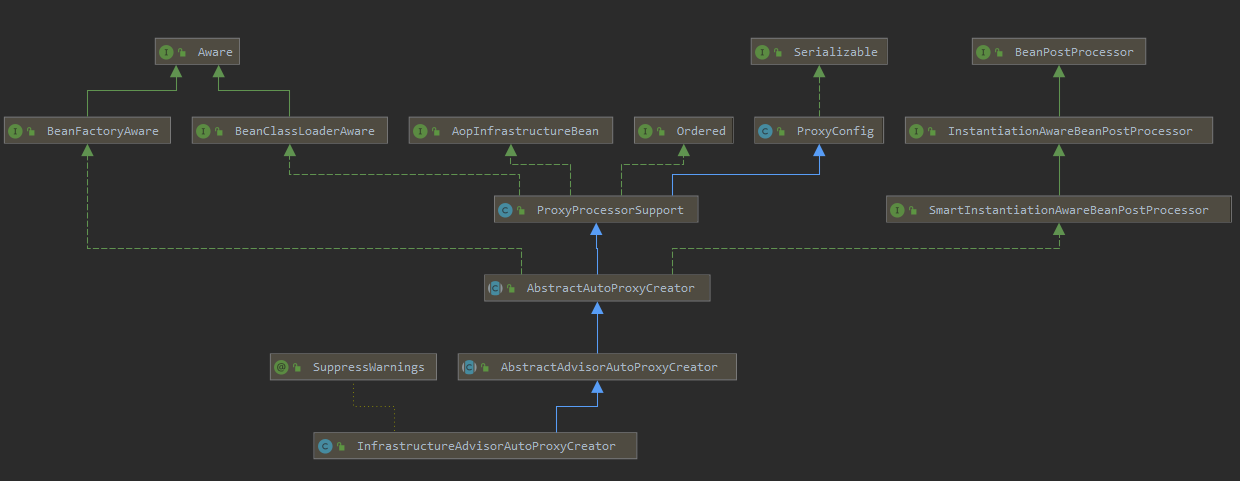
InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator 间接实现了
SmartlnstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ,而SmartlnstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessm 又继承InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor。,也就是说在Spring 中,所有bean 实例化时Spring 都会保证调用其postProcessAfterInitialization 方法。其实现是在父类AbstractAutoProxyCreator 类中实现。1//AbstractAutoProxyCreator23public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {4if (bean != null) {5Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);6if (!this.earlyProxyReferences.contains(cacheKey)) {7return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);8}9}10return bean;11}12//对指定的bean 进行封装13protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {14if (beanName != null && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {15return bean;16}17if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {18return bean;19}20//基础设施类和指定不需要代理的类则跳过包装21if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {22this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);23return bean;24}25// 获取类的增强器26// Create proxy if we have advice.27Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);28if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {29this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);30//创建代理31Object proxy = createProxy(32bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));33this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());34return proxy;35}3637this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);38return bean;39} - 以上方法目标:
- 找出指定类对应的增强器
- 依据增强器创建代理
获取对应class/method 增强器
- 功能:找出增强器,判断是否满足要求
1//AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator23protected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, TargetSource targetSource) {4List<Advisor> advisors = findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName);5if (advisors.isEmpty()) {6return DO_NOT_PROXY;7}8return advisors.toArray();9}10//获取所有符合要求的代理11protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {12//寻找候选增强器13List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();14//候选增强器中找到匹配项15List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName);16extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);17if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) {18eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);19}20return eligibleAdvisors;21}
对于事务属性的获取规则相信大家都已经很清楚,如果方法中存在事务属性,则使用方法上的属性,否则使用方法所在的类上的属性,如果方法所在类的属性上还是没有搜寻到对应的事务属性,那么再搜寻接口中的方法,再没有的话,最后尝试搜寻接口的类上面的声明。
总结
当判断某个bean 适用于事物增强时,也就是适用于增强器BeanFactoryTransactionA忧ributeSourceAdvisor ,所以说,在自
定义标签解析时,注入的类成为了整个事务功能的基础。
BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor 作为Advisor 的实现类,自然要遵从Advisor的处理方式,代理被调用时会调用这个类的增强方法,也就是此bean 的Advise , 又因为在解析事务定义标签时我们把Transactionlnterceptor 类型的bean 注入到了BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor 中,所以,在调用事务增强器增强的代理类时会首先执行
Transactionlnterceptor 进行增强,也就是在Transactionlnterceptor 类中的invoke 方法中完成了整个事务的逻辑。
事务增强器
- TransactionInterceptor 继承自 MethodINterceptor, 支撑着事物的整个逻辑。通过以上代码可知,事物的处理方式分为两种:
1//TransactionInterceptor23public Object invoke(final MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {4// Work out the target class: may be {@code null}.5// The TransactionAttributeSource should be passed the target class6// as well as the method, which may be from an interface.7Class<?> targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null);89// Adapt to TransactionAspectSupport's invokeWithinTransaction...10return invokeWithinTransaction(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass, new InvocationCallback() {1112public Object proceedWithInvocation() throws Throwable {13return invocation.proceed();14}15});16}1718//TransactionAspectSupport19protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, Class<?> targetClass, final InvocationCallback invocation)20throws Throwable {2122// If the transaction attribute is null, the method is non-transactional.23//获取事物对应的属性24final TransactionAttribute txAttr = getTransactionAttributeSource().getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass);25//获取beanFactory 中的TransactionManager26final PlatformTransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr);27//获取方法的唯一标识,(类.方法,如service.UserServicelmpl.save)28final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr);29// 声明式事物处理30if (txAttr == null || !(tm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) {31// Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls.32// 创建 transactionInfo33TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);34Object retVal = null;35try {36//执行被增强方法37// This is an around advice: Invoke the next interceptor in the chain.38// This will normally result in a target object being invoked.39retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();40}41catch (Throwable ex) {42//异常回滚43// target invocation exception44completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);45throw ex;46}47finally {48//清除信息49cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);50}51// 提交事物52commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);53return retVal;54}5556else {//编程式事物处理57final ThrowableHolder throwableHolder = new ThrowableHolder();5859// It's a CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager: pass a TransactionCallback in.60try {61Object result = ((CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager) tm).execute(txAttr,62new TransactionCallback<Object>() {6364public Object doInTransaction(TransactionStatus status) {65TransactionInfo txInfo = prepareTransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);66try {67return invocation.proceedWithInvocation();68}69catch (Throwable ex) {70if (txAttr.rollbackOn(ex)) {71// A RuntimeException: will lead to a rollback.72if (ex instanceof RuntimeException) {73throw (RuntimeException) ex;74}75else {76throw new ThrowableHolderException(ex);77}78}79else {80// A normal return value: will lead to a commit.81throwableHolder.throwable = ex;82return null;83}84}85finally {86cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);87}88}89});9091// Check result state: It might indicate a Throwable to rethrow.92if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {93throw throwableHolder.throwable;94}95return result;96}97catch (Exception ex) {98// .....99}100} - 声明式事物
- 编程式事物
事物处理的步骤:
- 获取事物的属性 - 事物的属性是事物处理的基石,
- 加载配置中的TransactionManager
- 不同的事物处理方式采用不同的逻辑
- 事物属性: 声明式事物需要有事物属性,编程式事物不需要事物属性
- TransactionManager: CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager 实现 PlatformTransactionManager接口,暴露一个方法用于处理事物的回调。
- 在目标方法执行前获取事物并且收集事物信息。
- 执行目标方法
- 一旦出现异常,处理异常信息 (spring 默认只回滚 RunTimeException)
- 事物提交前的事物信息处理
- 事物提交
事务创建
1 | //TransactionAspectSupport |
2 | protected TransactionInfo createTransactionIfNecessary( |
3 | PlatformTransactionManager tm, TransactionAttribute txAttr, final String joinpointIdentification) { |
4 | //如果没有指定名称,则使用方法唯一标识,并用 DelegatingTransactionAttribute 封装属性 |
5 | // If no name specified, apply method identification as transaction name. |
6 | if (txAttr != null && txAttr.getName() == null) { |
7 | txAttr = new DelegatingTransactionAttribute(txAttr) { |
8 | |
9 | public String getName() { |
10 | return joinpointIdentification; |
11 | } |
12 | }; |
13 | } |
14 | |
15 | TransactionStatus status = null; |
16 | if (txAttr != null) { |
17 | if (tm != null) { |
18 | //获取transactionStatus |
19 | status = tm.getTransaction(txAttr); |
20 | } |
21 | else { |
22 | if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { |
23 | logger.debug("Skipping transactional joinpoint [" + joinpointIdentification + |
24 | "] because no transaction manager has been configured"); |
25 | } |
26 | } |
27 | } |
28 | //依据属性与status 准备一个TransactionInfo |
29 | return prepareTransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status); |
30 | } |
事物的传播规则
PROPAGATION_REQUEST_NEW 表示当前方法必须在他自己的事物里面执行,方法执行前,必须创建新的事物,而如果之前有事物正在执行,则挂起之前的事物,从而执行当前的事物。当前的事物完成后,再将之前的事物还原。
PROPAGATION_NESTED 表示当前有事物正在执行,在方法执行前,必须创建一个
PROPAGATION_NESTED类型的事物,它是已经存在事务的一个真正的子事务. 潜套事务开始执行时, 它将取得一个 savepoint. 如果这个嵌套事务失败, 我们将回滚到此 savepoint. 嵌套事务是外部事务的一部分, 只有外部事务结束后它才会被提交.:- spring 中允许套嵌事物时,则首先设置保存点的方式作为异常处理的回滚,
- 对于其他方式,比如JTA 无法使用保存点的方式,那么处理方式与PROPAGATION_REQUIRES NEW 相同, 而一旦出现异常, 则由Spring 的事务异常处理机制去完成后续操作。
_区别_:
- PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW 启动一个新的, 不依赖于环境的 “内部” 事务. 这个事务将被完全 commited 或 rolled back 而不依赖于外部事务, 它拥有自己的隔离范围, 自己的锁, 等等. 当内部事务开始执行时, 外部事务将被挂起, 内务事务结束时, 外部事务将继续执行.
- PROPAGATION_NESTED 开始一个 “嵌套的” 事务, 它是已经存在事务的一个真正的子事务. 潜套事务开始执行时, 它将取得一个 savepoint. 如果这个嵌套事务失败, 我们将回滚到此 savepoint. 嵌套事务是外部事务的一部分, 只有外部事务结束后它才会被提交.
- 由此可见, PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW 和 PROPAGATION_NESTED 的最大区别在于, PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW 完全是一个新的事务, 而 PROPAGATION_NESTED 则是外部事务的子事务, 如果外部事务 commit, 潜套事务也会被 commit, 这个规则同样适用于 roll back.
事务回滚
- 当程序没有按照预期情况执行,那么会出现特定的错误,当出现错误的时候,spring 会出现回滚。具体执行如下:在对目标方法进行处理时,一旦出现Throwable 异常就会进入此方法,但并不是对所有的Throwable异常进行回滚,如,默认情况下, Exception 是不会被处理。
1//TransactionAspectSupport2protected void completeTransactionAfterThrowing(TransactionInfo txInfo, Throwable ex) {3if (txInfo != null && txInfo.hasTransaction()) {4if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {5logger.trace("Completing transaction for [" + txInfo.getJoinpointIdentification() +6"] after exception: " + ex);7}8//判断是否回滚: 默认的依据是抛出的异常是否是RunTimeException或者是error 类型9if (txInfo.transactionAttribute.rollbackOn(ex)) {10try {11//依据事物状态进行判断12txInfo.getTransactionManager().rollback(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());13}14catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {15logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex);16ex2.initApplicationException(ex);17throw ex2;18}19catch (RuntimeException ex2) {20logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex);21throw ex2;22}23catch (Error err) {24logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback error", ex);25throw err;26}27}28else {29//如果不满足回滚条件,即使抛出异常也会提交事物30// We don't roll back on this exception.31// Will still roll back if TransactionStatus.isRollbackOnly() is true.32try {33txInfo.getTransactionManager().commit(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());34}35catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {36logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", ex);37ex2.initApplicationException(ex);38throw ex2;39}40catch (RuntimeException ex2) {41logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", ex);42throw ex2;43}44catch (Error err) {45logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit error", ex);46throw err;47}48}49}50}
回滚条件
- 关键的地方就是在txlnfo.transactionAttribute.rollbackOn(ex)这个函数默认情况下Spring 中的事务异常处理机制只对RuntimeException 和Error 两种类型的异常进行处理。当然,我们也可以扩展来改变。 常用的方式是使用事物提供的属性设置,用注解的方式,如:
1// DefaultTransactionAttribute implements TransactionAttribute2public boolean rollbackOn(Throwable ex) {3return (ex instanceof RuntimeException || ex instanceof Error);4}1(propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED , rollbackFor=Exception.class)回滚处理
spring 在处理复杂逻辑的过程,首先会给出一个整体的处理脉络,把细节委托给其他函数去处理。1//AbstractPlatformTransactionManager implents PlatformTransactionManager2public final void rollback(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException {3//如果事物已经完成,再次回滚会抛出异常4if (status.isCompleted()) {5throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(6"Transaction is already completed - do not call commit or rollback more than once per transaction");7}89DefaultTransactionStatus defStatus = (DefaultTransactionStatus) status;10processRollback(defStatus);11}12//具体的回滚代码13private void processRollback(DefaultTransactionStatus status) {14try {15try {16// 激活所有的 TransactionSynchronization 中的方法17triggerBeforeCompletion(status);18if (status.hasSavepoint()) {19if (status.isDebug()) {20logger.debug("Rolling back transaction to savepoint");21}22//如果有保存点,也就是当前事务为单独的线程则会退到保存点23status.rollbackToHeldSavepoint();24}25else if (status.isNewTransaction()) {26if (status.isDebug()) {27logger.debug("Initiating transaction rollback");28}29//如果当前事务为独立的新事务,则直接回退30doRollback(status);31}32else if (status.hasTransaction()) {33if (status.isLocalRollbackOnly() || isGlobalRollbackOnParticipationFailure()) {34if (status.isDebug()) {35logger.debug("Participating transaction failed - marking existing transaction as rollback-only");36}37//// 如果当前事务不是独立的事务,那么只能标记状态, 等事物链链执行完毕后统一回滚38doSetRollbackOnly(status);39}40else {41if (status.isDebug()) {42logger.debug("Participating transaction failed - letting transaction originator decide on rollback");43}44}45}46else {47logger.debug("Should roll back transaction but cannot - no transaction available");48}49}50catch (RuntimeException ex) {51triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_UNKNOWN);52throw ex;53}54catch (Error err) {55triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_UNKNOWN);56throw err;57}58//激活所有TransactionSynchronization 中对应的方法59triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_ROLLED_BACK);60}61finally {62//清空记求的资源并将挂起的资源恢复63cleanupAfterCompletion(status);64}65}
- 自定义触发器的调用,包括在回滚前、完成回滚后的调用,当然完成回滚包括正常回滚与回滚过程中出现异常,向定义的触发器会根据这些信息作进一步处理,而对于触发器的注册,常见是在回调过程中通过TransactionSynchronizationManager 类中的静态方法直接注册:
public static void registerSynchronization(TransactionSynchronization synchronization) - 除了触发监听逻辑外,真正的就是回滚逻辑处理了
- 当之前已经保存的事务信息中有保存点信息的时候,使用保存点信息进行回滚。常用于嵌入式事务,对于嵌入式的事务的处理,内嵌的事务异常并不会引起外部事务的回滚。
- 当之前已经保存的事务信息中的事务为新事务,那么直接回滚。常用于单独事务的处理对于没有保存点的回滚, Spring 同样是使用底层数据库连接提供的API 来操作的。由于我们使用的是DataSourceTransactionManager ,那么doRollback 函数会使用此类中的实现:
- 当前事务信息中表明是存在事务的,又不属于以上两种情况,多数用于JTA ,只做回滚标识,等到提交的时候统一不才是交。
- 回滚后的信息清除
1//AbstractPlatformTransactionManager2private void cleanupAfterCompletion(DefaultTransactionStatus status) {3status.setCompleted();4if (status.isNewSynchronization()) {5TransactionSynchronizationManager.clear();6}7if (status.isNewTransaction()) {8doCleanupAfterCompletion(status.getTransaction());9}10if (status.getSuspendedResources() != null) {11if (status.isDebug()) {12logger.debug("Resuming suspended transaction after completion of inner transaction");13}14resume(status.getTransaction(), (SuspendedResourcesHolder) status.getSuspendedResources());15}16}
- 设置状态是对事务信息作完成标识以避免重复调用。
- 如果当前事务是新的同步状态,需要将绑定到当前线程的事务信息清除。
- 如果是新事务需要做些清除资源的工作。
- 如果在事务执行前有事务挂起,那么当前事务执行结束后需要将挂起事务恢复。
重置 TransactionInfo 中的 ThreadLocal 信息
- 略
事务提交
spring 的事物在执行过程中没有出现任何异常,则进行事物提交1//TransactionAspectSupport2protected void commitTransactionAfterReturning(TransactionInfo txInfo) {3if (txInfo != null && txInfo.hasTransaction()) {4if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {5logger.trace("Completing transaction for [" + txInfo.getJoinpointIdentification() + "]");6}7txInfo.getTransactionManager().commit(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());8}9} - 在真正的数据提交之前, 还需要做个判断,在我们分析事务异常处理规则的时候,当某个事务既没有保存点又不是新事务,Spring 对它的处理方式只是设置一个回滚标识。这个回滚标识在这里就会派上用场了,主要的应用场景如下。
- 某个事务是另一个事务的嵌入事务,但是, 这些事务又不在Spring 的管理范围内, 或者无法设置保存点,那么Spring 会通过设置回滚标识的方式来禁止提交,首先当某个嵌入事务发生回滚的时候会设置回滚标识,而等到外部事务提交时,一旦判断出当前事务流被设置了回滚标识, 则由外部事务来统一进行整体事务的回滚。
- 当事务没有被异常捕获的时候也并不意味着一定会执行提交的过程。说明:
1//AbstractPlatformTransactionManager2public final void commit(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException {3if (status.isCompleted()) {4throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(5"Transaction is already completed - do not call commit or rollback more than once per transaction");6}78DefaultTransactionStatus defStatus = (DefaultTransactionStatus) status;9//如果事物在事物链中已经被标记为回滚,则直接回滚10if (defStatus.isLocalRollbackOnly()) {11if (defStatus.isDebug()) {12logger.debug("Transactional code has requested rollback");13}14processRollback(defStatus);15return;16}17if (!shouldCommitOnGlobalRollbackOnly() && defStatus.isGlobalRollbackOnly()) {18if (defStatus.isDebug()) {19logger.debug("Global transaction is marked as rollback-only but transactional code requested commit");20}21processRollback(defStatus);22// Throw UnexpectedRollbackException only at outermost transaction boundary23// or if explicitly asked to.24if (status.isNewTransaction() || isFailEarlyOnGlobalRollbackOnly()) {25throw new UnexpectedRollbackException(26"Transaction rolled back because it has been marked as rollback-only");27}28return;29}30//提交事物处理31processCommit(defStatus);32}3334//实际体i骄傲方法35private void processCommit(DefaultTransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException {36try {37boolean beforeCompletionInvoked = false;38try {39//预留40prepareForCommit(status);41//添加的TransactionSynchronization 中对应方法的调用42triggerBeforeCommit(status);43//44triggerBeforeCompletion(status);45beforeCompletionInvoked = true;46boolean globalRollbackOnly = false;47if (status.isNewTransaction() || isFailEarlyOnGlobalRollbackOnly()) {48globalRollbackOnly = status.isGlobalRollbackOnly();49}50if (status.hasSavepoint()) {51if (status.isDebug()) {52logger.debug("Releasing transaction savepoint");53}54//如果存在保存点,则清除保存点55status.releaseHeldSavepoint();56}57else if (status.isNewTransaction()) {58if (status.isDebug()) {59logger.debug("Initiating transaction commit");60}61//如果是独立的 事物,则直接提交62doCommit(status);63}64// Throw UnexpectedRollbackException if we have a global rollback-only65// marker but still didn't get a corresponding exception from commit.66if (globalRollbackOnly) {67throw new UnexpectedRollbackException(68"Transaction silently rolled back because it has been marked as rollback-only");69}70}71catch (UnexpectedRollbackException ex) {72// can only be caused by doCommit73triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_ROLLED_BACK);74throw ex;75}76catch (TransactionException ex) {77// can only be caused by doCommit78if (isRollbackOnCommitFailure()) {79doRollbackOnCommitException(status, ex);80}81else {82triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_UNKNOWN);83}84throw ex;85}86catch (RuntimeException ex) {87if (!beforeCompletionInvoked) {88triggerBeforeCompletion(status);89}90doRollbackOnCommitException(status, ex);91throw ex;92}93catch (Error err) {94if (!beforeCompletionInvoked) {95triggerBeforeCompletion(status);96}97doRollbackOnCommitException(status, err);98throw err;99}100101// Trigger afterCommit callbacks, with an exception thrown there102// propagated to callers but the transaction still considered as committed.103try {104triggerAfterCommit(status);105}106finally {107triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_COMMITTED);108}109110}111finally {112cleanupAfterCompletion(status);113}114}
- 当事务状态中有保存点信息的话俊不会去才是交事务。
- 当事务非新事务的时候也不会去执行提交事务操作。
此条件主要考虑内嵌事务的情况,对于内嵌事务,在Spring 中正常的处理方式是将内嵌事务开始之前设置保存点, 一旦内嵌事务出现异常便根据保存点信息进行回滚,但是如果没有出现异常,内嵌事务并不会单独提交, 而是根据事务流由最外层事务负责提交,所以如果当前存在保存点信息便不是最外层事务, 不做保存操作,对于是否是新事务的判断也是基于此考虑。